In the home textile industry, particularly for curtains, bed sheets, duvet covers, sofa covers, and other wide-width fabrics, screen printing, direct-to-garment printing (digital inkjet printing), and heat transfer printing are three primary techniques used. Each technology has its unique advantages and limitations, and understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most suitable printing method for your products.
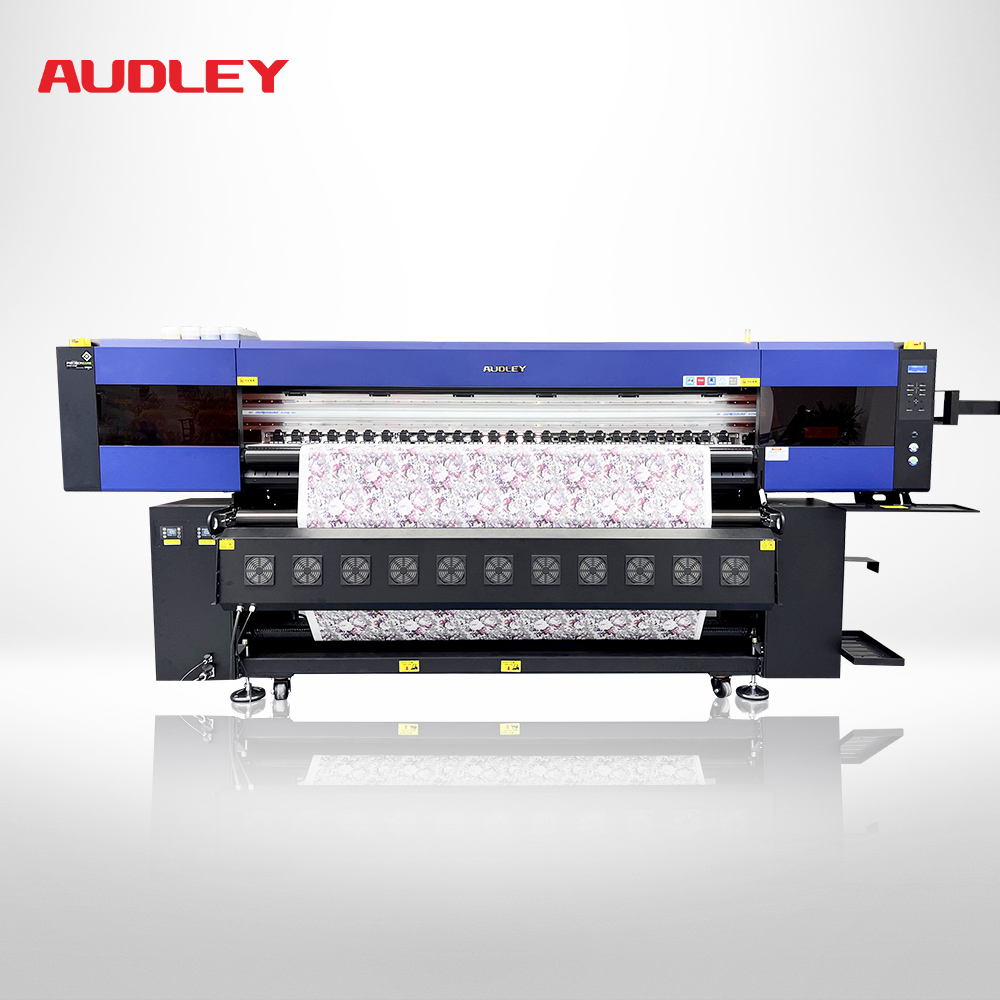

1. Pattern Detail and Color Representation
Screen Printing: Suitable for patterns with clear color blocks and fewer colors but limited in representing complex gradients or fine details.
Direct Inkjet Printing: Offers extremely high resolution, capable of perfectly presenting photo-level details, making it ideal for artistic floral designs or intricate decorative patterns.
Heat Transfer Printing: Includes sublimation (suitable only for synthetic fibers) and film transfer methods. The former features vibrant colors that penetrate into the fiber, while the latter leaves a coating on the fabric surface, generally less detailed than direct inkjet printing.
2. Applicability to Wide-Width Production
Screen Printing: Supports continuous wide-width fabric production but requires high precision equipment for large-scale multi-color overprinting.
Direct Inkjet Printing: The best choice, easily accommodating ultra-wide fabrics, perfect for large-sized home textiles.
Heat Transfer Printing: Limited by the width of transfer paper, requiring stitching during the process which can lead to misalignment and affect the beauty and quality of the finished product.
3. Production Costs and Economics
Screen Printing: Lowest cost for bulk simple pattern production but incurs high plate-making fees.
Direct Inkjet Printing: Optimal for small batches, complex patterns, saving on expensive plate-making processes.
Heat Transfer Printing: Moderate costs, no need for plate-making but increases the cost of transfer paper.
4. Fabric Applicability and Finished Product Feel
Screen Printing: Broad applicability but may result in a harder feel.
Direct Inkjet Printing: Best effect on natural fibers, maintaining the original softness and breathability of the fabric.
Heat Transfer Printing: Sublimation suitable only for polyester and similar synthetic fibers; film transfer sacrifices hand feel.
5. Environmental Friendliness and Durability
Screen Printing: Traditional pastes contain pollutants; washing produces considerable wastewater.
Direct Inkjet Printing: Utilizes water-based inks with low VOC emissions, demonstrating excellent environmental performance.
Heat Transfer Printing: Sublimation relatively environmentally friendly; film transfer generates plastic waste.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Recommendations based on different needs:
For bulk basic home textile products, prioritize screen printing.
For high-detail patterns, small batch flexibility, and environmental considerations, direct inkjet printing is recommended.
In specific cases, such as dealing with 100% polyester materials, sublimation heat transfer printing could be considered.
With technological advancements, digital inkjet printing is becoming mainstream due to its significant advantages in wide-width production, handling complex patterns, small batch flexibility, and environmental friendliness. It is expected to see broader applications in the home textile field in the future.
This translation provides an overview of the various printing technologies available for wide-width home textiles, highlighting their characteristics and suggesting appropriate choices based on specific requirements.




























